About Balkans

The Balkans (often referred to as the Balkan Peninsula although the two are not coterminous) is a geographic region of southeastern Europe. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains, which run through the centre of Bulgaria into eastern Serbia. The region has a combined area of 550,000 km2 (212,000 sq mi) and a population of about 55 million people.
"Balkan" comes from a Turkish word meaning "a chain of wooded mountains". The ancient Greek name for the Balkan Peninsula was the "Peninsula of Haemus”. The Balkans are also referred to as Southeastern Europe. The Balkan Peninsula may be defined as an area of southeastern Europe surrounded by water on three sides: the Adriatic Sea to the west, the Mediterranean Sea (including the Ionian and Aegean seas) to the south and the Black Sea to the east. Its northern boundary is often given as the Danube, Sava and Kupa rivers.
Countries which are geographically fully located within the Balkan peninsula: Albania, Bosnia & Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Greece, Macedonia and Montenegro. Countries which are significantly located in the peninsula: Croatia and Serbia (central part with Kosovo are on the Balkan; Vojvodina Province is on Panonian land-Central Europe). Countries which are located mostly outside the peninsula: Turkey, Slovenia and Romania.
History - The identity of the Balkans is dominated by its geographical position; historically the area was known as a crossroads of various cultures. It has been a juncture between the Latin and Greek bodies of the Roman Empire, the destination of a massive influx of pagan Slavs, an area where Orthodox and Catholic Christianity met, as well as the meeting point between Islam and Christianity. In pre-classical and classical antiquity, this region was home to Greeks, Illyrians, Paeonians, Thracians, Dacians and other ancient groups. Later the Roman Empire conquered most of the region and spread Roman culture and the Latin language but significant parts still remained under classical Greek influence. During the Middle Ages, the Balkans became the stage for a series of wars between the Byzantine, Bulgarian and Serbian Empires. Possibly the historical event that left the biggest mark on the collective memories of the peoples of the Balkans was the expansion and later fall of the Ottoman Empire. By the end of the 16th century, it had become the controlling force in the region, although it was centered around Anatolia. Many people in the Balkans and Carpathians place their greatest folk heroes in the era of either the onslaught or the retreat of the Ottoman Empire. Ottomans rulles over the most Balkan countries till the second half of 19th century. After this period the Austrohungarian Empire come in some Balkan countries, and the rest of country came independent, During the 20th century most important country on Balkan was been Yugoslavia. During the 1990s Yugoslavia was destroyed and new states has formed (Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia, Serbia, Montenegro and Macedonia).
Today, Balkan is one of the most interesting part of Europe. Grate cultural and historical heritage, ethno motives, food, vines, traditions… This is Balkan in short brief! This region is still undiscovered, although turisaticki has exceptional natural and cultural-historical themes worth attention!
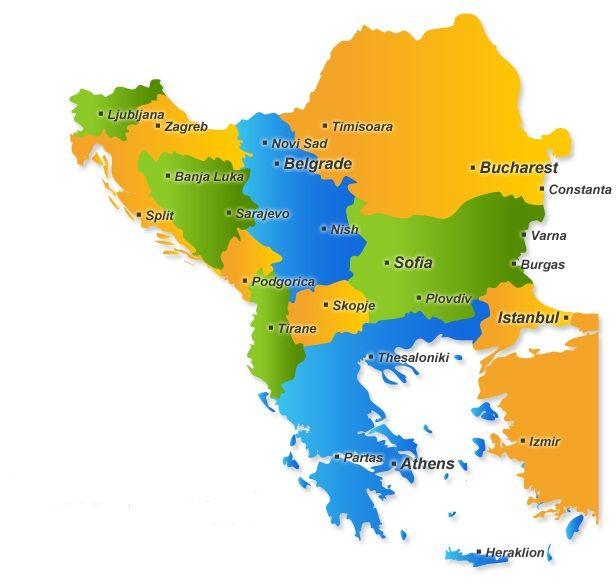
Map of Balkans



